Bony features of the clavicle

Bony Features of Clavicle
Boundaries and contents of the axilla.

boundaries and contents of the axilla.
Borders
- Apex – posterior border clavicle, lateral border of first rib and superior border of scapula
- Medial – serratus anterior, chest wall
- Lateral – intertubecular grove of humerus,
- Anteriorly – pec major and minor
- Posterioirly – subscapularis, teres major and lat dorsi, scapula
Smallest space when arm is fully abducted
Outlets
- mostly through inferiorly into arm.
- Quadangular space posteriorly – axillary nerve exits and post circumflex artery of humerus(subscapularis/teres minor above, teres major below, long head of triceps medially and humerus laterally)
- Clavipectoral traingle – pass cephalic vein and medial and lateral pectoral nerves (clavicle, pec major and deltoid)
- Triangular Interval – Contain radial nerve and profunda brachii artery, Borders Teras major superiorly, Long head of triceps medially, and humerus laterally.
Contents
- Axillary artery, vein, brachial plexus, tendons of biceps and corochobrachialis, Lymph nodes

Brachial plexus.
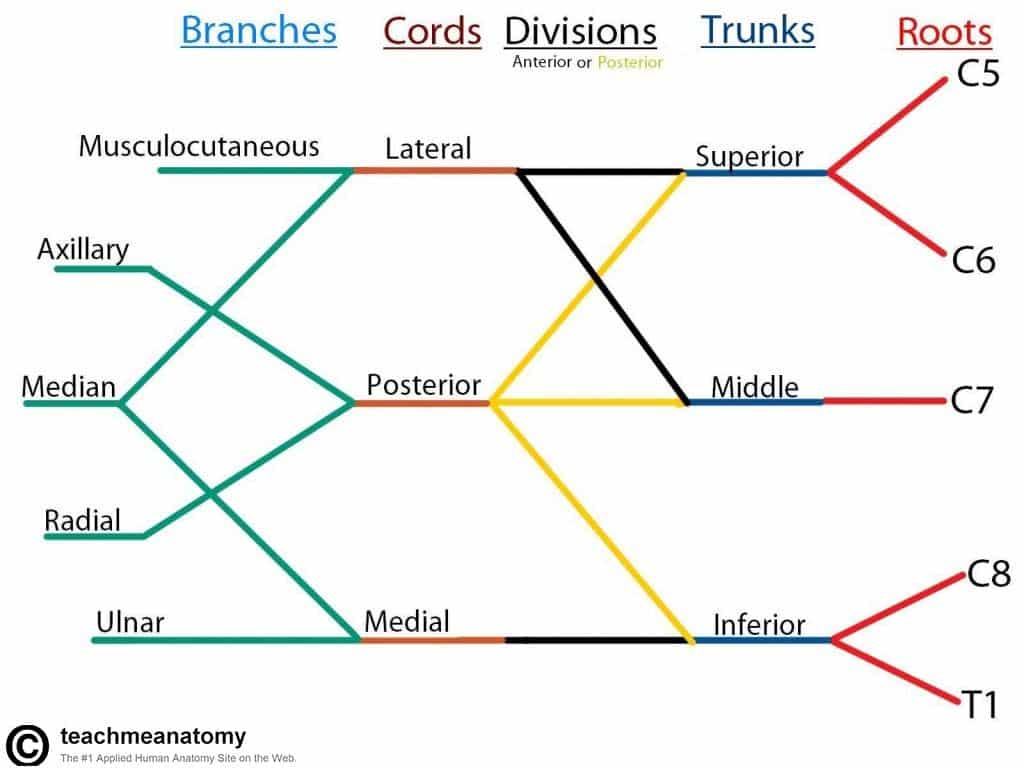
Brachial Plexus
Musculocutaneous Nerve
- Roots: C5, C6, C7.
- Motor Functions: Innervates the brachialis, biceps brachii and corocobrachialis muscles.
- Sensory Functions: Gives off the lateral cutaneous branch of the forearm, which innervates the lateral half of the anterior forearm, and a small lateral portion of the posterior forearm.
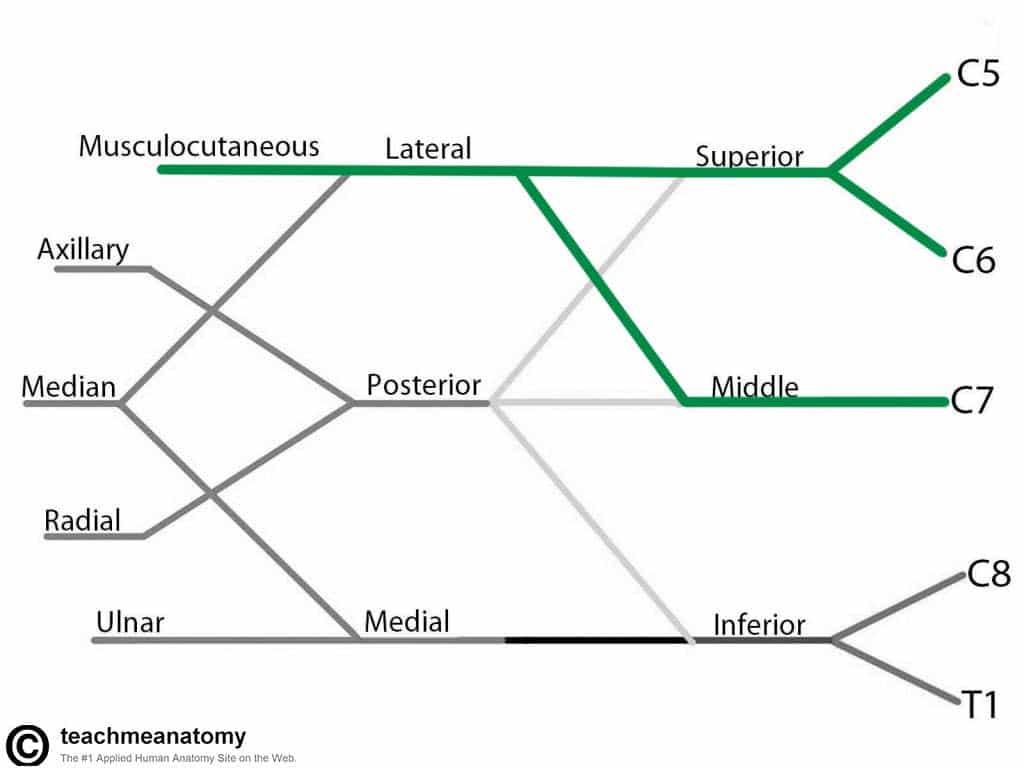
Musculocutaneous Nerve
Axillary Nerve
- Roots: C5 and C6.
- Motor Functions: Innervates the deltoid, teres minor and the long head of the triceps brachii.
- Sensory Functions: Gives off the superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm, which innervates the inferior region of the deltoid (“regimental badge area”).
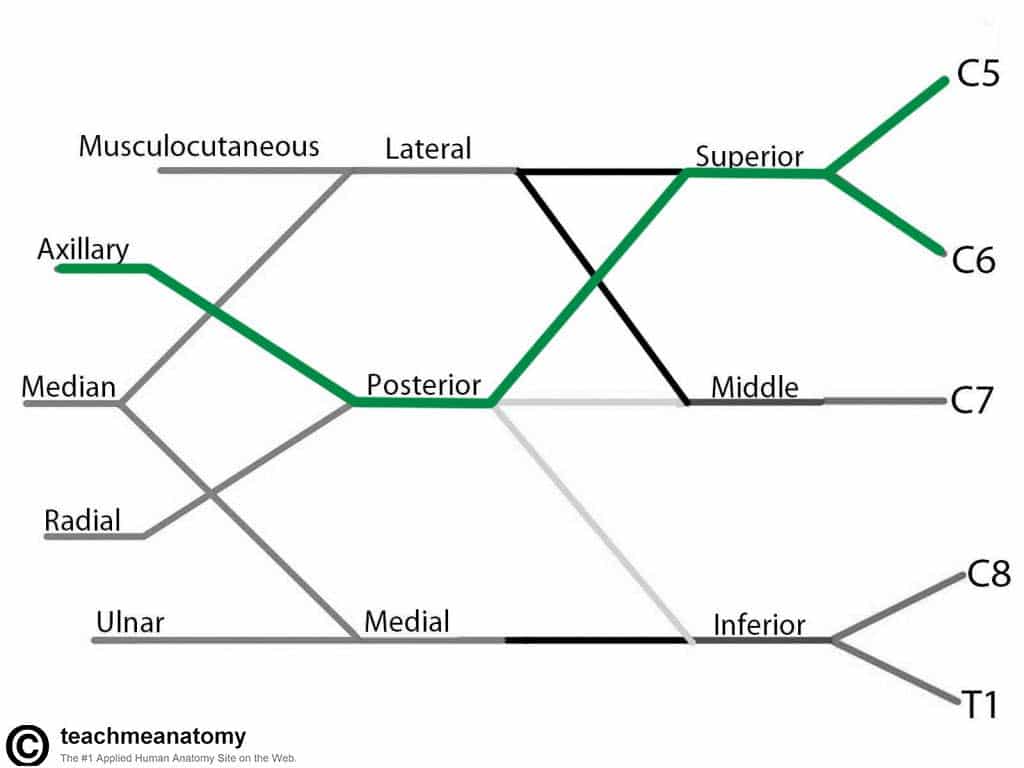
Axillary Nerve
Median Nerve
- Roots: C6 – C8 and T1.
- Motor Functions: Innervates most of the flexor muscles in the forearm, the thenar muscles, and the two lateral lumbrical muscles that move the index and middle fingers.
- Sensory Functions: Gives off the palmar cutaneous branch, which innervates the lateral part of the palm, and the digital cutaneous branch, which innervates the lateral three and a half fingers on the anterior (palmar) surface of the hand.
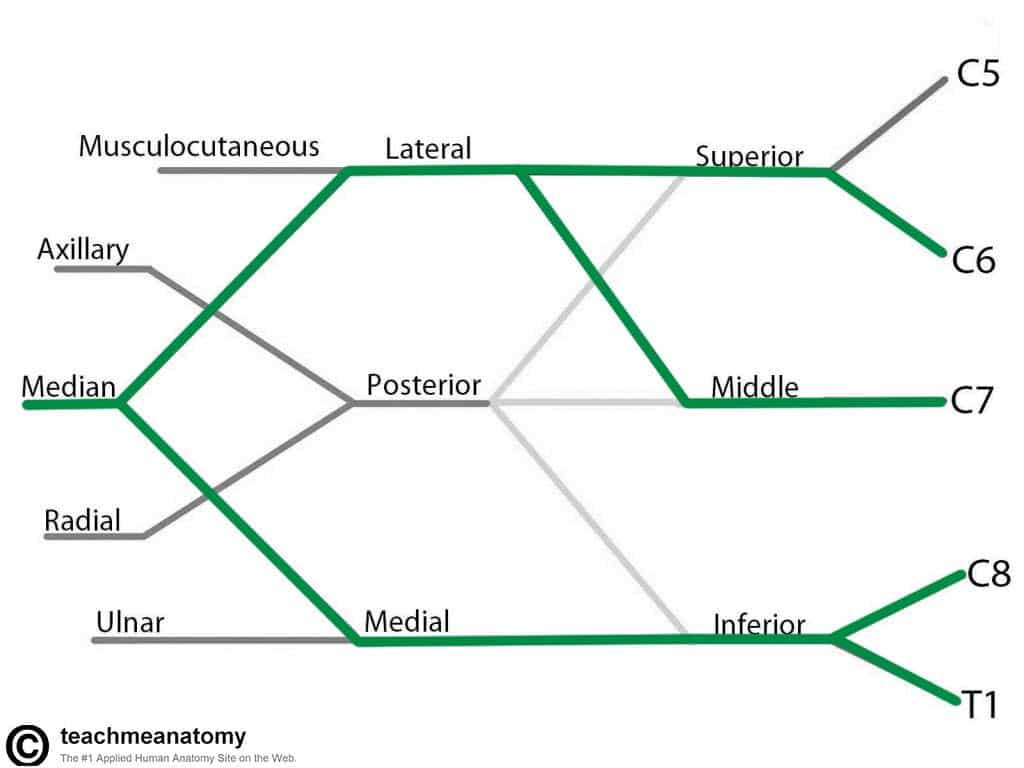
Median Nerve
Radial Nerve
- Roots: C5-C8 and T1.
- Motor Functions: innervates the triceps brachii, and the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm.
- Sensory Functions: Innervates the posterior aspect of the arm and forearm, and the posterior, lateral aspect of the hand.
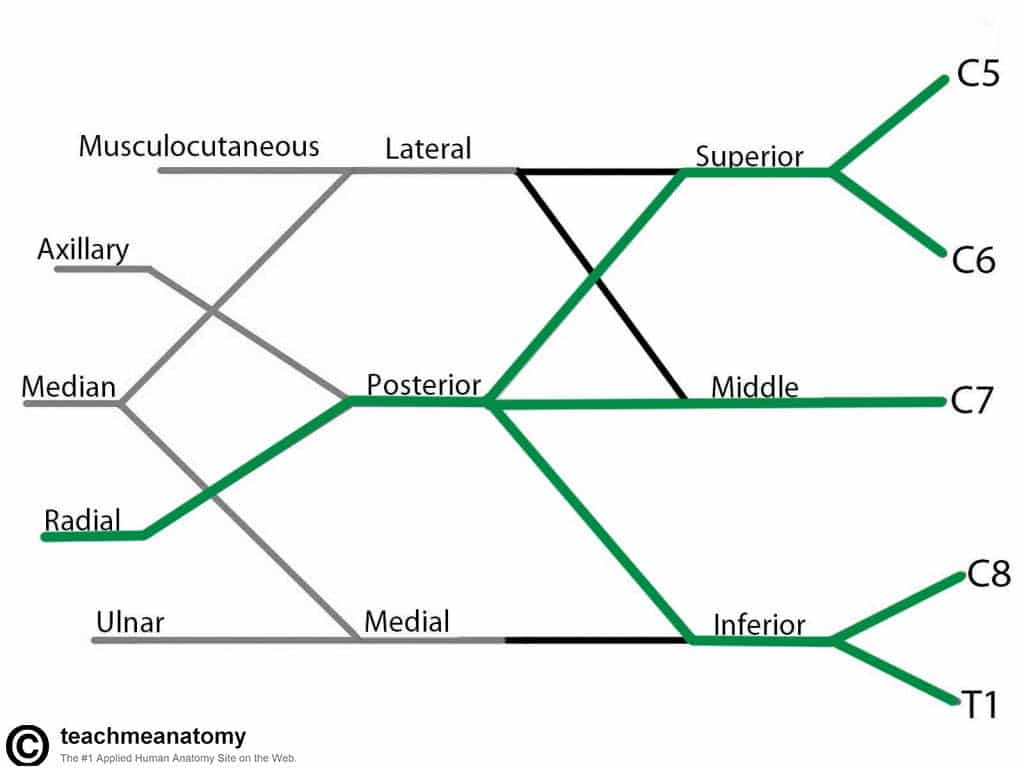
Radial Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
- Roots: C8 and T1.
- Motor Functions: Innervates the muscles of the hand (apart from the thenar muscles and two lateral lumbricals), flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of flexor digitorum profundus.
- Sensory Functions: Innervates the anterior and posterior surfaces of the medial one and half fingers, and associated palm area.
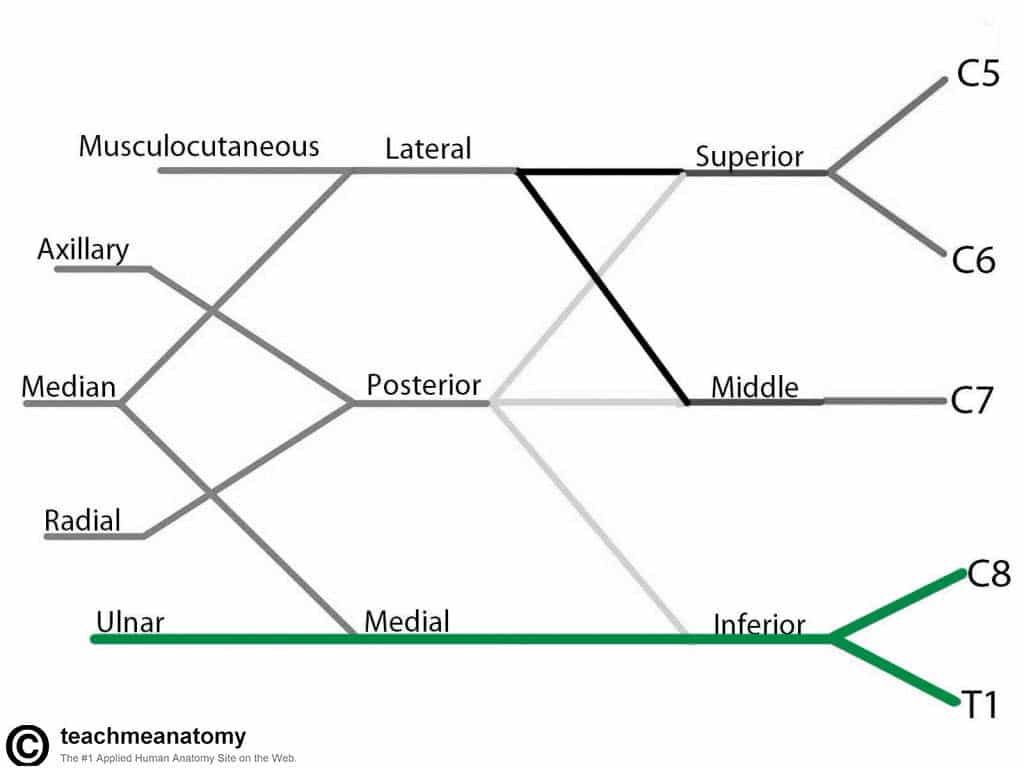
Ulnar Nerve
Sterno-clavicular joint.
- saddle type of synovial joint but functions as a ball-and-socket joint.
- The SC joint is divided into two compartments by an articular disc attaching to ant and post sternoclavicular ligaments.
- These ligaments as well as costoclavicular and interclavicular ligament give the joint stability +++ so rare to displace and also shock absorbs.
- Articular surface covered in fibrocartilage- articulates with manubrium and 1st costal cartilage.
- Movements – elevation 60o, rotation along longitudinal axis, AP of 25-30o, circumduction.
- Fractures most commonly post fall onto shoulder or outstretched hand – medial2/3 -lateral 1/3 junction.
- Fracture leads to lateral end being pulled medially and inferiorly and medial end pulled superiorly
- The superior displacement can damage suprascapular nerves and result in unopposed medial rotation of arm
Acromio clavicular joint
- Atypical plane synovial joint
- Articular surface covered in fibrocartilage and has an incomplete wedge articular disc.
- Acromioclavicular ligament
- Main stabiliser is external ligamnt – coracoclavicular ligaments – conoid and trapezoid ligaments which asre often seprated by a bursa.
- Only passive movement occurs at this joint.
- Lateral pec and axillary nerve, lateral supraclavicular nerve.
Branches of the axillary artery ?
- 3 parts – first medial to pec minor, 2nd posterior to pec minor and 3rd lateral to pec minor.
Send The Lord to Say A Prayer
1 – Superior Thoracic
2 – Thoraco acromial
3 – Lateral thoracic
4 – Subscapluar
5 – Anterior circumflex of humerus
6 – Posterior Circumflex of humerus

First division – one branch: (1) Supreme Thoracic Artery Second division – two branches: (2) Thoracoacromial (with four smaller branches) A. Pectoral Branch B. Deltoid Branch C. Acromial Branch D. Clavicular Branch (3) Lateral Thoracic Artery Third division – three branches: (4) Subscapular Artery (branches to the Circumflex Scapular Artery and the Thoracodorsal Artery) (5) Anterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (6) Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (which passes through the quadrangular space)
Subclavian artery – related to anterior scalene
- Starts from arch of aorta(at level of T4) or brachiocephalic trunk(behind Right SC joint). Travels between anterior and middle scalene muscles. Finishes at lateral border of first rib.
- In relation to scalene anterior:
- Medial – vertebral, internal thoracic, thyrocervical trunk(very short and divides in thyroid artery, transverse cervical and suprascapular artery)
- Posterior – costocervical trunk, sometimes dorsal scapular.
- Lateral – sometimes dorsal scapular.
Lymph nodes of the axilla.
- Superficial lymph follows superficial veins and deep follow deep.
- Efferent vessels from cubital lymph nodes ascend in the arm and terminate in the humeral (lateral) axillary lymph nodes.
- Most superficial lymphatic vessels accompanying the cephalic vein cross the proximal part of the arm and the anterior aspect of the shoulder to enter the apical axillary lymph nodes; however, some vessels previously enter the more superficial deltopectoral lymph nodes.
- Deep lymphatic vessels, less numerous than superficial vessels, accompany the major deep veins in the upper limb and terminate in the humeral axillary lymph nodes.
- Axillary LN clearance can endanger long thoracic nerve and result in winged scapula

Lymph drainage of the breast.
- 75% of Lymph drain to axillary LN (pectoral) and apical LNs
- Rest drain to internal thoracic LNs and contralateral breast and contralateral Axillar lymph nodes.