Acute renal failure:
Pre renal causes
- Hypovolaemia, hypotension, CCF –> poor renal perfusion–> decreased renal clearance of toxins and ischaemia of tubular cells
Intra renal causes
- Primary Glomerulonephritis
- Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis
- Postinfectious (Post strep – IgG mediated)
- Other
- Rapidly progressive (crescentic) glomerulonephritis
- Membranous nephropathy
- Minimal-change disease
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
- Dense deposit disease
- IgA nephropathy
- Chronic glomerulonephritis
- Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis
- Systemic Diseases with Glomerular Involvement
- HTN –> focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- DM –> tubulointerstitial fibrosis, hyalinizing arteriolar sclerosis, papilary necrosis.
- immunological – SLE, good pastures, wegners, HSP (rapidly progressive, crescents), microscopic polyangitis
- Amyloidosis
- Hereditary Disorders
- Alport, Fabry
- Nephritic syndrome – haematuria, uremia, variable proteinuria, oliguria, oedema and HTN
- Nephrotic syndrome – Proteinuria(>3.5g), hypoalbuminaemia, hyperlipidaemia, lipiduria.
- Major Changes observed in Glomerular diseases
- Histological changes – hypercellularity, BM thickening, Hyalinisation/sclerosis,
- Ab-Ag complex deposit mainly subendothelially
- antiGBM deposit in GBM
- Heymann – antibody to ag in epithelial cell.
- Ab –> cytotoxic injury and complement mediated injury –> epithelial cell foot process effacement and detachment–> increased leakage into urine of blood components.
| Disease | Pathogenesis | Glomerular Pathology | Most Frequent Clinical Presentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post strep | Circulating or planted antigen | IgG and C3 in GBM | Acute nephritis |
| Good pastures | Anti GBM | Proliferation, cresents | Rapidly progressive GN |
| Membranous | Insitu Ab mediated | Diffuse cap wall thickening | Nephrotic syn |
| Minimal change | Podocyte injury | Normal, lipid in tubule | Nephrotic syn |
| Focal segmental | Unknown | Focal and segmental sclerosis and hyalinosis | Nephrotic syn |
| Membrane proliferative | Immune complex | Mesangial proliferation, BM thickening | Nephrotic syn |
| Ig A nephropathy | Unknown | Focal proliferative GN | Recurrent haematuria or proteinuria |
| Chronic GN | Variable – mainly rapidly progressive and focal glomerulosclerosis | Hyalinized glomeruli | Chronic renal failure |
Post renal causes (Causes of urinary obstruction) –> back flow –> renal damage and decreased function.
- Renal Calculi
- Types
- Calcium oxalate and phosphate 70%
- Struvite 15-20%
- Uric acid 5-10%
- Cysteine 1-2%
- Complications.
- Pain, infection, renal failure,
- Ureteric stricture
- Types
- BPH
- Posterior urethral valves
- Tumours
- Inflammation – prostatitis, urethritis, retroperitoneal fibrosis
- Sloughed pappilae/blod clots
- Pregnancy
- Cystocoele
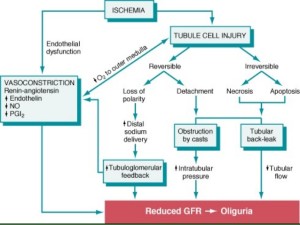
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN):
- Commonest cause of AKI – 50%
- Destruction of tubular epithelial cells and acute renal failure
- Causes
- Ischaemia, hypoperfusion
- Direct toxic injury – contrast, radiation, gentamycin
- Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis -hypersensitivity to drugs
- DIC
- Urinary obstruction
- Necrosis is more in PCT and PST in toxic type and less in ischaemic type. Both have casts from DCT to CD.
- Clinical course
- Initiation: 36hrs, slight decrease in UO and rise in blood urea.
- Maintanence: sustained oliguria, rising Urea and creatinine, hyper K, metabolic acidosis, uraemia – needs supportive mangement to carry pt over this
- Recovery: increasing UO, tubules still damaged so large amount of water and electrolytres lost – Hypo K, increase risk of infection, everything normalises eventually.
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI):
- Causes
- Haematologenous – Staphylococcus, E Coli
- Ascending – E Coli, Proteus, enterobacter
- Consequences
- Dysuria, frequency
- Pyelonephritis – flank pain, fever, acute renal failure.
- Predisposing factors
- Female – short urethra
- Vescioureteric reflux – shallow angle of ureter insertion.
- Instrumentation of urinary tract
- Pregnancy
- DM
- Immunosuppression
Chronic renal failure:
- HTN
- DM
- GN
Haemolytic-Uraemic syndrome.
- Childhood type – associated with bloody diarrhoea caused by intestinal infection by verocytotoxin releasing bacteria
- Adult
- Infection- typhoid, ecoli, shigellosis
- Antiphospholipid Abs
- Cx of preg and contraceptive
- Vascular renal disease eg HTN, scleroderma
- Chemo and immunosuppressive drugs
- Radiation
- Mechanism: endothelial injury–> activation–> intravascular thrombosis–> platelet aggregation–> distal ischaemia
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP):
- Fever, neurological sx, haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenic purpura, thrombi in glomeruli.
- Gene defect in ADAMTS-13–> affect cleavage of vWF –> promotion of platelet aggregation.
- Women, younger than 40
- Neurological sx are dominant.