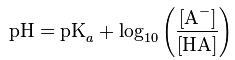Week 13 Physiology
Reaction between Hb and O2.
- O2 in blood is mainly attached to Hb but also is dissolved at a rate in proportion to PaO2. 0.003ml/mmHg (Henry’s law)
O2 – Hb dissociation curve: (This is important).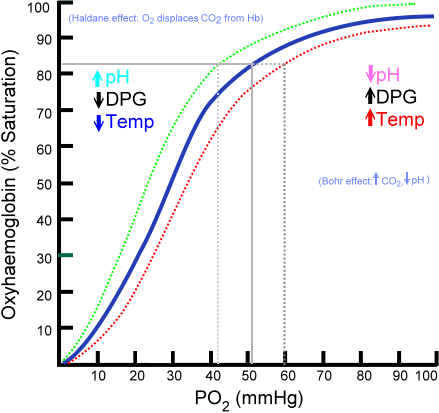
- OxyHb curve is the one that shifts. Upto 50mmHg the rise in O2 sats is fast then flattens out
- 40mmHg – 75%, 100mmHg – 97%
- Anaemia doesn’t affect O2 Sats but it does affect O2 concentration (amplitude of curve is less) so Hb can off load easier in tissue.
- Right shift (think hot, acidic, hypercarbic, hypoxic low DPG muscle)
- Even a small amount of CO causes L shift
Be able to draw it and plot in some values
- PO2/ SaO2
- 10 10
- 20 35
- 26 (P50) 50
- 40 75
- 50 80
- 60 90
- 70 92
- 80 94
- 90 96
- 100 98
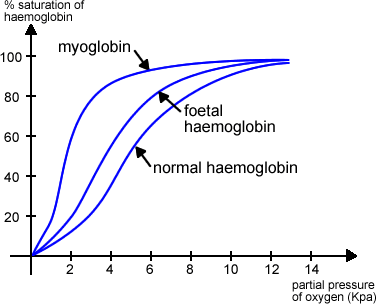
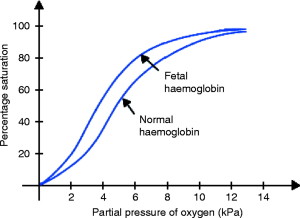
Be able to draw dissociation curves for Myoglobin and foetal Hb.
Buffers:
- Definition – a weak acid or base which acts to maintain the pH at a chosen value(7.4)
- Main buffers in vivo.
- Bicarbonate
- Ammonia
- Phosphate
- haemaglobin
CO2 transport.
- CO2 is carried in blood as
- Dissolved (10%)
- Bicarbonate (60%)
- Carbonic anhydrase in RBC speeds it up
- Chloride shift/Hamburger effect
- When H2CO3 formed it spontaneously disassociated into HCO3- and H+. H+ cant diffuse as easily, but HCO3 can diffuse out, to replace the anion, Cl- comes in.
- Combined with proteins as carbamino compounds(30%)
- CO2 dissociation curve is steeper and more linear than O2, moves depending on O2 saturation to R with increasing sats.
- The Haldane effect is a property of haemoglobin. Deoxygenation of the blood increases its ability to carry carbon dioxide, and for Hydrogen ions. Conversely, oxygenated blood has a reduced capacity for carbon dioxide. Helps load CO2 in periphery and unload CO2 in the lung.
Viva questions:
- Tell me about the structure of haemoglobin.
- 2 pairs of globin with haem molecule (not expected to draw the structure)
- Tell me about the reaction of Hb with O2.
- Draw the Hb-O2 dissociation curve.
- What are the advantages conferred by it’s non-linear shape ? (See West).
- What factors move the curve, and in which direction ?
- What is the definition and typical value of the P50 ? 26mmHg
- What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation ?
- For HA + H2O –> HO3+ + A-
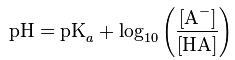
- What is the definition of a buffer ?
- What are the main buffers in the body ?
- Tell me about CO2 transport.
- Draw the CO2 dissociation curve
- What is the chloride shift ?
- What is the Bohr effect
- Hb/O2 affinity is inversely proportional to CO2 and acidity
- What is the Haldane effect