Cell types in Islets of Langerhans
- Insulin – B – 68%
- Glucagon – a – 20%
- Somatostatin – d – 10% (inhibit other 2)
- Pancreatic polypeptide – f cells
- 1-2% of pancreas
Insulin
- Structure.
- 2 chains of amino acids joined by a disulfide bridge
- Synthesis / secretion.
- Initially synthesised as preproinsulin then cleaved to insulin by time of release.
- Made in RER –> packaged in membrane bound granules in golgi appatatus and transported out via exocytosis and then enters blood vessel via fenestrations
- Effects.
- Liver
- Decrease ketogenesis
- Muscle
- Increase ketone uptake
- Adipose
- Increase fatty acid synthesis
- Increase TG deposition
- Inhibit hormone sensitive lipase.
- Liver
- Mechanism of action
- T 1/2 5mins
- Insulin binds to insulin receptors –>tyrosine kinase activity of receptor in tracellular side–> autophosphorylation of beta sub units of insulin receptor–> activation of phosphatidyl ionositol 3-kinase –> anabolic effect and increases glucose transporters etc
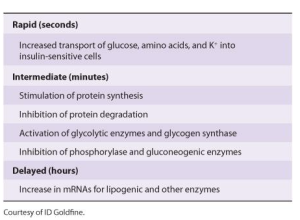
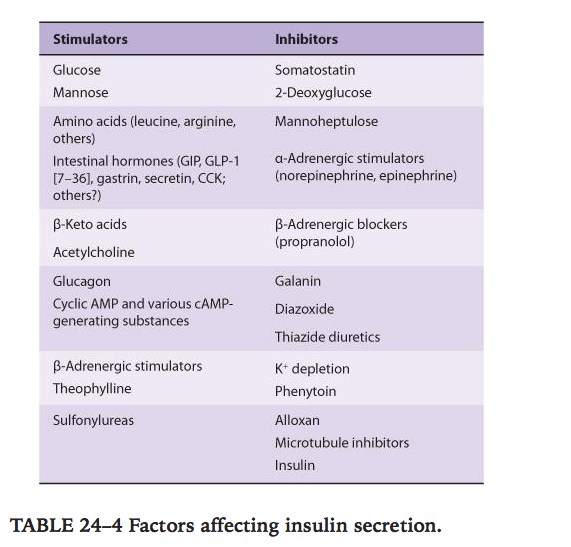
- Factors affecting insulin secretion.
Glucagon:
- Actions
- –> increase plasma glucose
- Increase glycogenolysis
- Increase gluconeogenesis
- Increase protein break down
- Increase lipolysis
- Increase ketogenesis
- Acts via G protein receptor –> adenyl cyclese–> increase cAMP –> increase activity of protein kinase A
- Can also activate phosphokinase C –> increase Ca2+
- In large doses its positively ionotropic
- Stimulates secretion of growth hormone, insulin and somatostatin
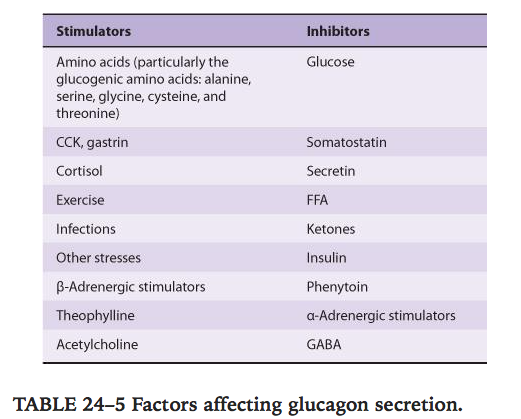
- Factors affecting secretion.
Somatostatin:
- Actions.
- Paracrine way to inhibit secretion of insulin, glucagon and pancreatic polypeptide
- Factors affecting secretion.
- Increased by glucose, amino acids(esp arginine and leucine), and CCK.
Pancreatic polypeptide.
- Secreted – cholinergic stimuli, protein containing meal, fasting, exercise, hypoglycaemia
- Inhibited – somatostatin, glucose
- Action – slows absorption of food
Basic overview of “Endocrine regulation of carbohydrate metabolism”.
Exercise promotes insulin independent increase of GLUT4 channels in muscle –> increased insulin sensitivity and can prompt hypoglycaemia in diabetics
- Catecholamine
- B agonists –> increase intracellular cAMP
- A agonists –> increase intracellular Ca2+
- In liver this causes increased glucose release –> hyperglycaemia initially
- Later glycogen synthesis
- FFA release
- Thyroid hormones
- Increase Glucose absorption from GIT, increase insulin breakdown and increase glycogenolysis in liver
- Diabetogenic
- Glucocorticoids
- The glucocorticoids are necessary for glucagon to exert its gluconeogenic action during fasting. They are gluconeogenic themselves, but their role is mainly permissive.
- In deficiency, fasting can precipitate hypoglycaemia.
- Growth hormone
- Worsens diabetes
- Increases FFA, decreases glucose uptake into cells, increase hepatic glucose output–> hyperglycaemia–> stimulate insulin release
Pancreas
- Retroperitoneal organ
- Secretes 2-2.5L per day
- Proenzymes
- Tryprsinogen
- Chymotrypsinogen
- Procarboxypeptidase
- Proelastase
- Kallikreinogen
- Phospholipase A
- Conversion of proenzymes requires conversion of trypsinogen to tripsin by duodenal enteropeptidase.
- Enzymes released in active form
- Lipase
- amylase
Viva questions:
- Tell me about the endocrine functions of the pancreas.
- Tell me about the exocrine functions of the pancreas.
- Tell me about insulin.
- Tell me about the actions of insulin.
- What factors affect insulin secretion ?
- How does insulin work ?
- Tell me about Glucagon.
- What factors affect glucagon secretion ?
- Tell me about control of blood glucose level