Adrenal morphology / architecture (MCQs).
- Adrenal medulla surrounded by cortex
- Medulla is 28% of total mass – has adrenaline secreting cells(larger with less dense granules) and noradrenaline secreting cells (smaller with very dense granules)
- Cortex has three sections, from outer – zona glomerulosa (15%), zona fasciculata(50%), zona reticularis (7%)
- All 3 secrete corticosteroid, only zona Glomerulosa secretes aldosterone, the other 2 secrete sex hormone
- Venous sinus exists interlaced between all sections
Adrenal medulla:
- Substances secreted and their effects.
- Adrenaline & Noradrenaline
- Glycogenolysis in liver and skeletal muscle
- Mobilisation of FFA
- Stimulate metabolic rate
- Positive ionotrope and chronotrope via B1 receptor
- Increase myocardial excitability
- Increase alertness
- NA –> peripheral vasoconstriction via A1 receptor
- Increase systolic and diastolic BP –> baroreceptors –> bradycardia –> decrease CO
- Adrenaline dilate blood vessels in liver and skeletal muscle via B2 receptor
- Drop peripheral resistance –> widening pulse pressure –> HR and CO increase
- Dopamine
- Renal and mesenteric vasodilation
- Elsewhere vasoconstriction
- Positive ionotrope via B1
- Increase SBP
- Natriuresis via ? Inhibiting NaK ATPase
- Adrenaline & Noradrenaline
- Regulation of medullary secretion.
- Stimulation by sympathetic preganglionic nerves
- Increased when standing
- After adrenalectomy, NA levels unchanged but adrenaline levels drop to near zero.
- Adrenal cortex and Substances secreted.
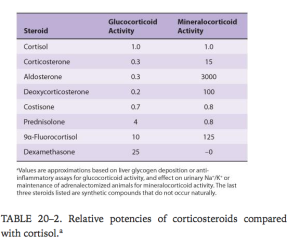
- Cortisol/corticosterone
- Testosterone/oestrogens – DHEA, androstenedione
- Mineralocorticoid – aldosterone
ACTH.
- From anterior pituitary
- Binds G protein receptor on adrenocortical cells –> activate adenyl cyclase –> increase cAMP –> increased cortisol and aldosterone formation
- Controls glucocorticoid, mineralocoticoid and sex hormone release from adrenal cortex
- Increases sensitivity of adrenal to subsequent catecholamines.
- Secreted in bursts (Circadian rhythm) so high in early morning.
Steroids
- Glucocorticoids are pretty important (use Cortisol as prototype).
- When bound glucocorticoid+steroid compound becomes a transcription factor that promote transcription of parts of the DNA to cause its effects
- Physiological effects
- Increase protein catabolism
- Increase glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis –> increase BSL
- Insulin resistance
- Permissive action – low amount of Glucocorticoid needed for catecholamines to exert their calorigenic effects, vasopressor effects, lipolytic effects. Very important to have vascular reactivity.
- Needed for water excretion
- Decrease circulating lymphocytes, eosinophils and basophils
- Inhibit ACTH secretion(neg feedback)
- Pathological effects
- Immunosuppressant
- HTN
- Hyperglycaemia
- Central adiposity
- Proximal myopathy
- Buffalo hump, moon facies,
- Striae
- Bruising, skin fragility
- Poor wound healing
- Irritability
- Insomnia
- Inability to concetrate
- osteoporosis
Aldosterone actions and factors affecting secretion.
- Increases Na reabsorption in kidney and increase H2O retention as a result. Also increase Na absorption from sweat, saliva and colon contents.
- Act on principal cells to increase activity of NaK counter transport and on intercalated cells to increase H+ ATPase –> high K and acidic urine.
- Release stimulated by ACTH, Angiotensin II(renin) by another G protein receptor and activation of protein kinase C, and high plasma K+.
- Aldosterone itself bind to its receptor and transcribes DNA to exert its effect.
Pituitary:
Know which hormones come from where and the functions of each.
- Anterior pituitary
- F: FSH – basophil
- L: LH – basophil
- A: ACTH- BASOPHILS
- T: TSH -basophil
- P: PROLACTIN – acid
- i: ignore ACIDOPHILS (“acid pig”)
- G: GH – acid
- Posterior pituitary
- Vassopressin
- oxytosin
Overview of growth hormone.
- 50% of active growth hormone is plasma protein bound
- Promotes long bone growth when ephiphyseal plate is not fused
- When in excess causes acromegaly – most viscera enlarged, high plasma protein levels.
- Lipolysis
- Na retention
- Decreased insulin sensitivity
- IGF -1 – pro growth but is antilipolytic and has insulin like activity
- Increase GH secretion
- Hypoglycaemia
- Starvation
- Exercise
- Stress
- Increased amino acids
- Protein meal
- Glucagon
- Vasopressin
- Androgens and oestrogens
- Decrease GH secretion
- REM sleep
- Cortisol
- Glucose
- FFA
- Medroxyprogesterone
- GH and IGF-1 (neg feedback)
Viva questions:
- What substances are secreted in the adrenal medulla ?
- How is their secretion controlled ?
- What substances are secreted in the adrenal cortex ?
- What do glucocorticoids do ?
- Tell me about Aldosterone.