WBC functions (broad concepts)
Innate immune system – does not require previous sensitisation to attack a foreign protein
- Macrophages
- Neutrophils
- Barriers
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Natural Killer cells
- Complement system
Humoural immunity
- B lymphocytes – bind to antigen on MHC II molecules, each B cell has a different antigen receptor(Ab), once bound it becomes activated and increase in number and can specialise into plsama cells which secrete Abs
- Ab opsonise, activate complement and start inflammation or inactivate the target without causing cell damage or inflammation
- T helper cells assist
- Aimed at extracellular antigens
Cellullar immunity
- T lymphocytes
- CD8 cells identify antigens in MHCI molecules and become activated and kill the cell if foreign/tumour material is identified in MHC I
- Activation is assisted by T helper cells
- Aimed at intracellular pathogens and tumours
Complement
- Cascade of proteins from 1 -9
- MAC complex – C5b-C9 puts holes in antigen membranes
- C5a – chemotaxis, leukocyte adhesion, activation, migration, and inflammation via increased vasc permeability(histamine release)
- C3b – opsonises
- C3a – anaphylotoxin – trigger degranulation of endothelial cells, mast cells or phagocytes – if localised it is inflammation, if generalised it can be similar to anaphylaxis
- Classical pathway
- Activated by Ag – Ab complex
- Alternative pathway
- stim by microbial surface molecules
- Lecithin pathway
- stim by plasma mannose binding lectin binds to carb on bacterial
- All pathways cleave and activate C3 – most abundant one.
Cytokines (broad concepts)
- Attracts immune cells – gradient generated leads to chemotaxis
- Assists in activation of immune cells eg IL4, IL1, TNF a
- Contributes to immune response eg fever
Viva questions:
- How is the Immune System organised ; i.e. what are it’s major components ?
- What is the body’s response to an antigen ?
- What is the MHC ? What is it’s role ?
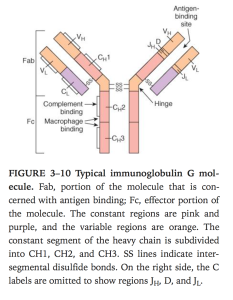
- Draw an immunoglobulin molecule.
- Long chain
- Short chain
- F constant(Fc) at bottom and F variable(Fab) at top(to bind different antigens)
- Describe the complement system.
- What are anaphylatoxins and what is their role ?
- Tell me about the classical/alternative pathway.
- What are cytokines and what do they do ?