Root of neck:
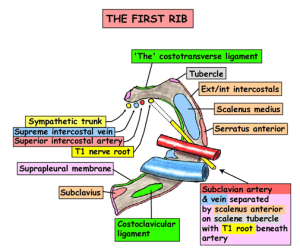
- 1st ribs and costal cartilage, manubrium, body of T1
- Relations of neck of first rib
Subclavian vein and its relations
- Continuation of axillary vein, starts at lateral border of 1st rib and ends at IJV(medial end of clavicle to become Brachiocephalic vein – joint where thoracic duct and R lymphatic trunk drain).
- Passes over 1st rib ant to scalene tubercle parallel to subclavian artery, seperated by ant scalene muscle
- Receives EJV
- Can do central line with infraclavicular approach – midpoint of clavicle and directed towards jugular notch of manubrium. The aim is below head of SCM. Risk puncturing SC artery and pneumothorax.
Subclavian artery
- Seperated by anterior scalene into medial, posterior and lateral sections
- Medial(1st) – vertebral artery, internal thoracic and thyrocervical trunk
- Posterior (2nd)- costocervical branch
- Transverse cervical and suprascapular artery may come from 2nd or third part instead of coming from thyrocervical trunk.
Basic understanding of fascia / tissue spaces.
- Platysma in subcutaneous tissue
- First deep investing fascia contains SCM and trapezius
- Pretracheal – thyroid, parathyroid, trachea, oesophagus, infrahyoid muscles- sternothyroid and strenohyoid.
- Prevertebral – vertebral column and muscles eg long colli
- Carotid sheath – CC, IC, IJV, vagus, deep cervical LNs, carotid sinus nerve, sympathetic nerve fibres.
- Carotid sheath, pretracheal fascia and retropharyngeal space all communicate with mediastinum.
Sternomastoid (as an important landmark with lots of relations).
- Divides anterior and lateral triangle- sternocleidomastoid region of neck lies inbetween the two heads.
- SCM region – SCM, sup EJV, greater auricular nerve, transverse cervical nerve. Lesser supraclav fossa – inf IJV.
Posterior Cervical region:
- Boundaries – ant border of trapezius
- Contents – trapezius, cutaneous posterior rami of cervical nerves
Posterior triangle:
- Border – posterior border of SCM and ant border of trapezius. Superior and inferior triangles seperated by inferior belly of omohyoid.
- Occipital triangle – par t of EJV, post branches of cervical plexus nerves, CNXI, trunks of brachial plexus, transverse cervical artery, Cervical LN
- Omoclavicular triangle- SC artery(3rd part), SC vein, suprascapular artery, supraclavicular LNs.
Anterior triangle:
- Boundaries – midline, inferior mandible, ant border of SCM
Contents:
- The submental triangle, inferior to the chin, is a suprahyoidarea bounded inferiorly by the body of the hyoid and laterally by the right and left anterior bellies of the digastric muscles. the apex of the submental triangle is at the mandibular symphysis.
- Contains submental LNs
- The mandibular triangle/digastric triangle boundaries include mandible, anterior and posterior bellies of digastric
- Contains ramifying branches of CN7. myohyoid and hyoglossus muscles in floor.
- The carotid triangle: sternocleidomastoid, posterior belly of digastric and superior belly of omohyoid
- Contains – CC, IC, IJV, vagus, and accessory nerve. Hypoglossal and ansa cervicalis of cervical plexus are in front and sympathetic trunk, recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior thyroid artery is behind.
- Muscular triangle: sternocleidomastoid, superior belly of omohyoid and midline from hyoid bone to jugular notch
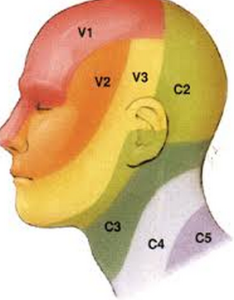
Dermatomes of the neck
Front of the neck
(i.e. structures of importance when doing a surgical airway).
- Skin–> sub cut–> platysma–> vertical strap muscles–> cricothyroid membrane
- Skin –> retract strap muscles and thyroid isthmus–> cut between ring1 or 2 to ring 4. Insert tracheostomy tube.
- Inferior thyroid veins descend on ant trachea, 10% of people have a midline thyroid ima artery from brachiocephalic trunk, L brachiocephalic vein is in danger,
Thyroid gland.
- Level c5-T1, isthmus at 2nd or 3rd tracheal ring
- Blood supply
- Subclavian –> Thyrocervical trunk -> inf thyroid artery bilaterally(largest branch of trunk)
- External carotid–> superior thyroid artery–> ant and post branches.
- Veins
- Superior and middle veins drain into IJV
- inferior thyroid vein–> brachiocephalic vein.
- Nerve supply
- vasomotor only, secretion controlled by pituitary
- Thyroid cartilage –
Larynx
- Level C3-6
- Thyroid, cricoid, epiglotis
- 3 paired – arytenoid, corniculate(most medial), cuneiform
- Thyroid cartilage superior border opposite c4
- Thyrohyoid membrane
- Cricothyroid joints.
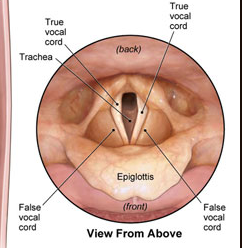
- Vestibular fold is superior to vocal folds and combined with quadrangular membrane forms ariepiglottic fold.
- Piriform recess laterally for fluids to go down.
Muscles – all supplied by inferior laryngeal nerve from recurrent laryngeal except cricothyroid.
- Posterior cricoarytenoid – abducts vocal cords
- Vocalis – relaxes posterior VC while tensing anterior vocal cord
- Cricothyroid lengthens vocal cords – external laryngeal nerve(CNX)
- Thyroaretenoid – relaxes VC –
- Lateral cricoarytenoid – adducts VC
Great vessels of the neck (CCA/ECA/ICA/IJV):
Surface anatomy.
- Jugular notch – jugular venous arch
- Lesser supraclav fossa(between sternal and clavicular heads of SCM)- inferior IJV
- Vertical across SCM to angle of mandible – EJV – made obvious with valsalva
- Deep to superior half of SCM – cervical plexus
- Deep to inferior half of SCM – IJV, CCA, and vagus nerve in carotid sheath.
- Great supraclavicular fossa/omoclav triangle – 3rd part of subclavian artery
- Path of SC artery – Sternoclavicular joint to midpoint of clavicle in arch.
- CNXI – intersection between sup and middle third of posterior border of SCM and inf and middle third of ant border of trapezius.
- Carotid sheath – SC joint to point midway between mastoid process and angle of mandible.
Nerves in neck
- Phrenic runs on anterior scalene
- Vagus runs in carotid sheath as posterior structure
- R recurrent laryngeal nerve turns under R subclavian artery
- L recurrent laryngeal nerve turns back under arch of aorta
Branches of ECA:
Before the external carotid enters the parotid gland, it gives off six branches, three from in front, two from behind and one deep (medial). In front are the superior thyroid artery, lingual artery and facial artery. Behind are the occipital artery and the posterio-auricular artery. Medially is the ascending pharyngeal artery.
- Some: Superior thyroid artery
- Anaesthetists: Ascending pharyngeal artery
- Like: Lingual artery
- Fun: Facial artery
- Others: Occipital artery
———above all arise in carotid triangle——–
- Prefer: Posterior auricular artery
- S &: Superficial temporal artery (terminal branch)
- M: Maxillary artery (terminal branch)