Overview of lymphatic drainage of head & neck.
- There are no LN in either scalp or face so all drain to submental, submandibular, parotid, mastoid and occipital LN.
- Deep LN along IJV–> thoracic duct on left and jugular lymphatic trunk on right –> IJV/brachiocephalic vein.
Meninges.
- Dura mater
- Sub dural space – venous sinuses
- Arachnoid Mater
- Itself is avascular and doesn’t receive nerve supply
- Sub arachnoid space – CSF, cerebral arteries
- Pia Mater – on the brain parenchyma intimately
Ventricular system of the Brain
- Lateral ventricles to 3rd is via foramen munro.
- CSF generated in mainly 3rd and 4th ventricle by choroid plexus(ependymal cells) but occurs in all. 400ml/d
- 3rd –> 4th via cerebral aqueduct
- 4th–> subarachnoid space via lateral foramen
- CSF reabsorbed by arachnoid granulations –> veins.
Blood supply of the cerebral hemispheres
- Internal carotid start at C4–> carotid canal –> cavernous sinus –> middle cerebral and anterior cerebral, opthalmic artery and post communicating
- Middle cerebral splits in to anterior and posterior
- Anterior then has anterior communicating branch to link to other side
- Sublcavian medial to ant scalene–> Vertebral arteries–> transverse foramina–> foramen magnum–> meningeal branch, ant and post spinal arteries, PICA–> basilar artery –> posterior cerebral –> posterior communicating artery.
- ACA – anteromedial brain
- MCA – lateral brain
- PCA – occiput
Under pterigion is the ant division of middle meningeal artery – meeting point of 4 bones – frontal, parietal, temporal and sphenoid.
Venous drainage
- Dural venous sinuses – between periosteal and dural layers of dura mater.
- Drain brain and meninges
- Sigmoid sinus –> internal jugular vein –> jugular foramen, deep to SCM, lateral to common carotid–> brachiocephalic vein
- Superior sagital sinus
- Inferior sagittal sinus
- Straight sinus
- Occipital sinus
- Superior and inferior petrosal sinus
- Cavernous sinus:
- Lateral to body of sphenoid
- Receives venous drainage from sup and inf opthamic, middle superficial cerebral, sphenoparietal sinus
- Internal carotid and CN6 crosses this sinus
- CN3,4,V1and V2 are all in lateral wall.
- At risk of infection from facial vein(valveless) can lean to Cavernous sinus thrombosis–> blindness and other CN defects.
Osteology of the skull:
- frontal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- temporal bone
- sphenoid bone
- zygomatic bone
- lacrimal bone
- nasal bone
- palatine bone
- ethmoid bone
- maxilla, mandible
Orbit:
- Roof – frontal bone, lesser wing of sphenoid
- Medial – lacrimal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxilla
- Lateral – zygomatic, greater wing of sphenoid
- Floor – maxilla, palatine, zygomatic
- Apex – optic foramen
- Optic canal – optic nerve + opthalmic artery
- Superior orbital fissure – lacrimal, frontal, trochlear (CN IV), oculomotor (CN III), nasociliary and abducens (CN VI) nerves. It also carries the superior ophthalmic vein.
- Inferior orbital fissure – inferior opthalmic vein, maxillary nerve(CN5), sympathetic nerves.
- Supraorbital foramen carries – supraorbital nerve(CNV1)
Control of the pupil / pupillary reflexes (Important).
- Pupillary dilation – sympathetic
- Pupillary constriction – CN3, via parasympathetic ciliary ganglion
- Accomodation – CN3 – via sympathetic
- Levetor palpabrae superioris – CN3
Facial muscles (overview only).
- All inervated by facial nerve
- Occipitofrontalis, orbicularis occuli, orbicularis oris, buccinator, levetor labii superioris
Facial nerve (Important):
- Supplies muscle of facial expression, platysma, auricular muscles, scalp muscles.
- Extracranial course- Starts at stylomastoid foramen–> posterior auricular nerve–> parotid gland –> parotid plexus–> 5 branches “Two Zulus Buggered My Cat”
- Temporal – superior part of orbicularis oculi
- Zygomatic – inferior part of orbicularis oculi
- Buccal – external to buccinator to supply it and also supplies upper lip muscles.
- Marginal mandibular – risorius, lower lip and chin. Passes deep to platysma
- Cervical – platysma supply.
Sensory nerve supply of face.
- Spinal cutaneous nerves C2, C3 – posterior scalp behind auricles
- Great auricular nerve – inferior auricle, parotid region
- V1 Opthalmic – via superior orbital fissure–> frontal, nasociliary, lacrimal nerves.
- V2 Maxillary – foramen rotundum–> pterygopalatine fossa –> branch to pterygopalatine ganglion–> inferior orbital fissure –> orbit–> infraorbital grove–> infraorbital nerve. Zygomaticotenporal branch gives supply to lacrimal nerve?
- V3 Mandibular/has motor component.–> foramen ovale–> mental, auricotemporal and buccal branches. Auricotemporal supplies parotid.
Muscles of mastication – motor root of trigeminal
- Masseter
- Temporalis, medial and lateral pterygoids.
Blood supply of face
- Facial is the main. All are from external carotid. All anastamose with each other and across midline.
- Facial – EC–> deep to submandibular gland, winds around inferior border of mandible to enter face.
- Occipital – EC–> passes medial to posterior belly of digastric and mastoid process, accompanies optic nerve in occiput region.
- Posterior auricular – EC–> deep to parotid and along styloid process.
- Supraorbital and supratrochlear –> from IC via opthalmic artery.
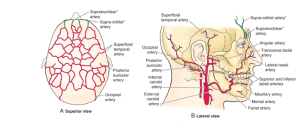
Blood supply of nose (particularly septum).
5 arteries
- ant and post ethmoid(opthamlic)
- sphenopalatine(maxiallary)
- greater palatine(maxillary)
- superior labial(facial).
Nasal meatus
- Superior – posterior ethmoidal sinuses open
- Middle – frontal sinus via ethmoidal infundibulum, maxillary sinus
- Inferior – nasolacrimal duct
- Sphenoethmoidal recess – superoposterior to superior concha receives sphenoidal sinus.
Venous drainage of face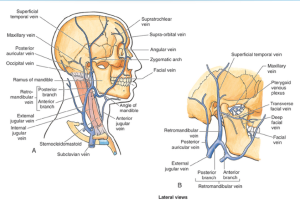
Valveless and all partnering arteries. Drain to cavernous sinus as well as IJV.
Supratrochlea+supraorbital = angular vein at root of nose
Angular becomes facial at inferior margin of orbit
Facial joins IJV opposite or inferior to level of hyoid.
Layers of scalp.
- Skin
- Connective tissue – sub cutaneous layer – dense
Aponeurosis - Loose connective tissue
- Periosteum
Nerve and blood supply of scalp.
- Arteries in Sub cutaneous layer with anastamoses. Walls stuck to Connective tissue so cant constrict much therefore cuts BLEED!!!
- IC – superatrochlear and supraorbital
- EC – posterior auricular, occipital, superficial temporal
What passes through the various foramina of the skull?
- Anterior cranial fossa
- Foreamen cecum – nasal emissary vein
- Cribriform plate – CN1
- Anterior and posterior ethmoid foramina – vessels and nerves of same name
- Middle Cranial fossa
- Optic canal – CN2, opthalmic artery
- Superior orbital fissure – V1, CN3, CN4, CN6, sympathetic fibres, opthalmic veins
- Foramen rotundum – V2
- Foramen ovale – V3, accessory meningeal artery and vein
- Faramen spinosum – middle meningeal artery and vein, meningeal branch of V3.
- Foramen lacerum – Internal carotid and accompanying venous plexus and sympathetic plexus.
- Groove/hiatus of greater petrosal nerve – greater petrosal nerve, petrosal branch of middle meningeal artery\
- Stylomastoid foramen – CN7
- Posterior cranial fossa
- Foramen magnum – medulla, meninges, CNXI, vertebral arteries, dural veins, ant and post spinal arteries.
- Jugular foramen – IJV, CN 9,10,11, inferior petrosal and sigmoid sinuses, ascending pharyngeal and occipital arteries.
- Hypoglossal canal – CN12
Parotid
- Innervation – V3 branch auriculotemporal, glossopharyngeal(CN9) for parasymp secretomotor via otic ganglion
- Sym from external carotid plexus
Lacrimal
- V2 zygomatic branch
- Parasym stim from CN7(greater petrosal nerve) via pterygopalatine ganglion
- Sym from internal carotid plexus
- Empties in inferior nasal meatus.
Muscles of mastication and their attachments
- Temporalis – floor of temporal fossa and fascia –> tip and medial surface of coronoid process and ant ramus of mandible – elevates jaw
- Masseter – inferior border and medial surface of maxillary process of zygomatic bone and arch –> angle and lateral surface of ramus of mandible – elevate mandible
- Lateral pterygoid – two heads, infratemporal and crest of greater wing of sphenoid, lateral pterygoid plate–> joint capsule and articular disc of TMJ, pterygoid fovea on mandible – protract mandible and depresses chin. Unilateral contraction causes jaw to swing to contralateral side.
- Medial pterygoid – 2 headed, medial part of lateral pterygoid, tuberosity of maxilla –> medial surface of ramus of mandible – acts synergistically with masseter to elevate mandible. Protrusion of jaw.
Tongue
- Posterior 1/3 – both sensory and taste by CN9
- Ant 2/3 taste – CN7
- Ant 2/3 sensory – CN5 via lingual nerve